In today’s digital landscape, email security is more critical than ever, with over 94% of organizations experiencing email-related security incidents in 2023. Encryption stands out as a powerful defense, ensuring sensitive information stays protected. As the most widely used email platform, Gmail has introduced enhanced security features to help safeguard your data.
This guide will walk you through the process of sending an encrypted email using Gmail’s Confidential Mode, while also exploring whether there are more robust alternatives for protecting your communications.
Why Encryption is Important in Email Communication
Think about what happens to your email when you hit “send.” If it’s not secure, it could easily end up in the wrong hands—whether that’s cybercriminals, hackers, or even just unintended recipients.
Sensitive information, such as financial records, patient details, or legal documents, is especially at risk.
Emails are easy targets because they pass through multiple servers and networks before reaching the recipient. Each stop creates an opportunity for interception or tampering. That’s where encryption steps in. Encryption transforms the content into a secure, unreadable format, accessible only to the intended recipient.
An encrypted email is better than an unencrypted one in several ways:
- Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Provides peace of mind for both sender and recipient.
- Enhances trust in professional and confidential communications.
- Complies with security standards and regulations (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR).
Gmail’s Encryption Options
Gmail uses a default standard encryption method called TLS (Transport Layer Security), which is designed to protect your messages while they’re moving between sending and receiving servers.
However, TLS has its limitations. While it encrypts the data during transfer, it doesn’t secure the message itself—only the connection. This means that if the receiving server doesn’t have strong security, your email could still be vulnerable.
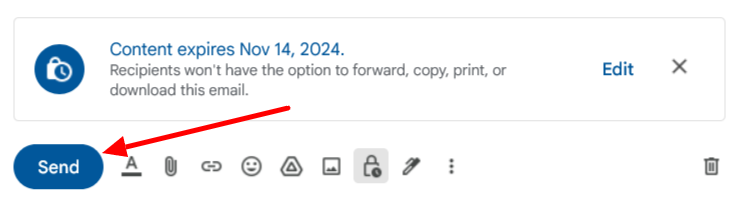
To enhance security, Gmail introduced “Confidential Mode” in beta on June 25, 2019. This feature adds an extra layer of protection with options like:
- No Forwarding or Downloading: Emails sent in Confidential Mode can’t be forwarded, downloaded, copied, or printed.
- Expiration Dates: You can set an expiration date so the email automatically becomes inaccessible after a set period.
- Password Protection for Non-Gmail Users: For recipients who don’t have a Gmail account, Confidential Mode can require a passcode.
How to Send an Encrypted Email Using Gmail’s Confidential Mode
Here’s a quick guide to sending an encrypted email with Gmail’s Confidential Mode:
Step 1: Open Gmail and compose a new email.
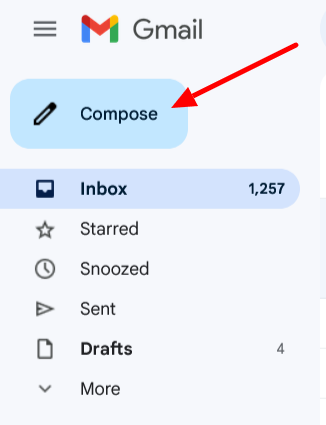
Step 2: Click on the “Confidential Mode” icon at the bottom of the email window.
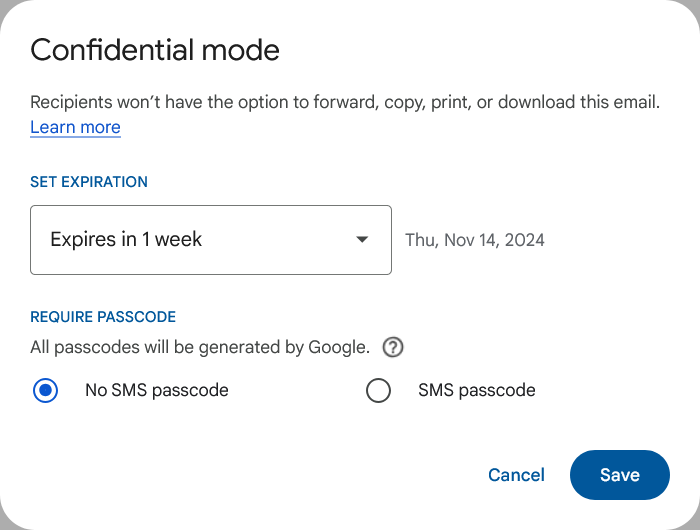
Step 3: Set expiration date and passcode options.
Step 4: Write your email message and click “Send.”
Optional: For extra security, select an SMS passcode to require a passcode. Click Save to return to your composed email.
Limitations of Gmail’s Encryption
Even with Confidential Mode, Gmail’s encryption has some limitations:
- Stored on Gmail Servers: While confidential emails may be inaccessible to recipients after expiration, copies can still be stored on Gmail’s servers.
- No Full End-to-End Encryption: Gmail’s encryption doesn’t protect emails all the way from sender to recipient, leaving some potential vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability to Screenshots: Recipients can still take screenshots of emails, which undermines confidentiality.
- No Scheduling with Confidential Mode: You can’t use Gmail’s scheduling feature for emails sent in Confidential Mode.
- Access Issues: Some recipients may be unable to open Confidential Mode emails if they expire before being read or if the passcode phone number is from an unsupported region, as only certain countries are currently supported.
These limitations make Gmail’s Confidential Mode useful but not entirely secure for highly sensitive information. That’s why third-party tools with full end-to-end encryption can enhance email security, offering better data protection and peace of mind.
Using Third-Party Tools for End-to-End Encryption in Gmail
End-to-end encryption is a stronger security measure because it protects your email from the moment you send it until it reaches the recipient—no one in between, including email servers, can access it.
For those needing this higher level of encryption, here are some third-party tools that integrate well with Gmail:
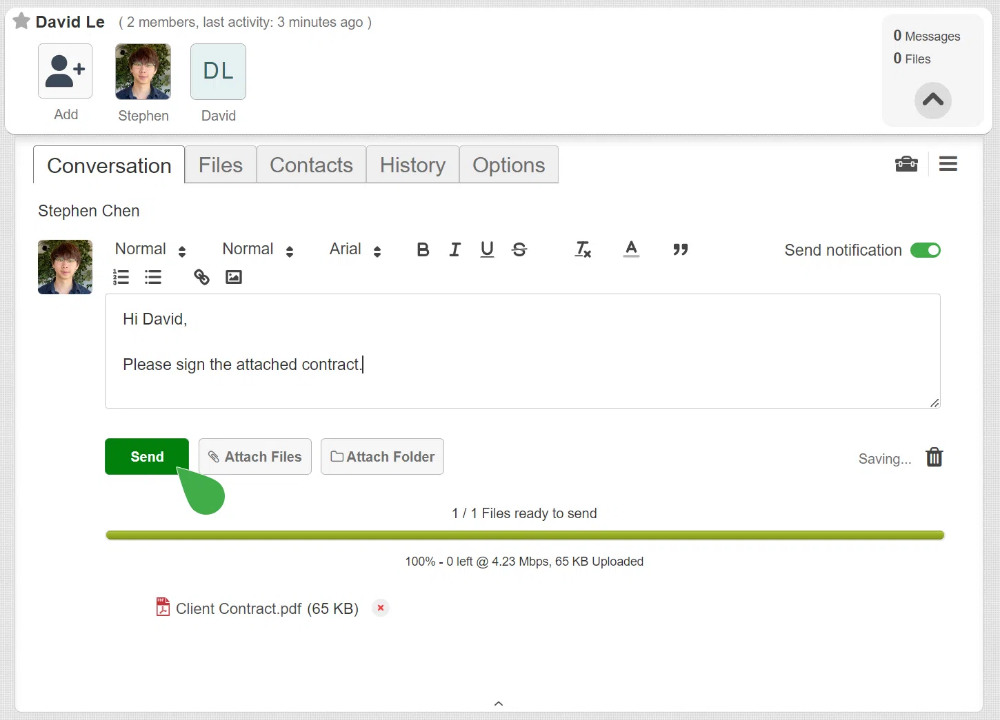
1. Titanfile
Among the tools for email security, TitanFile stands out as a secure, intuitive platform designed for safely sharing files.
TitanFile offers an intuitive solution for large file transfers, reliable tracking, and top-level security—all in one platform. With a free 15-day trial, TitanFile makes it easy to test these features without commitment.
Here’s how it works:
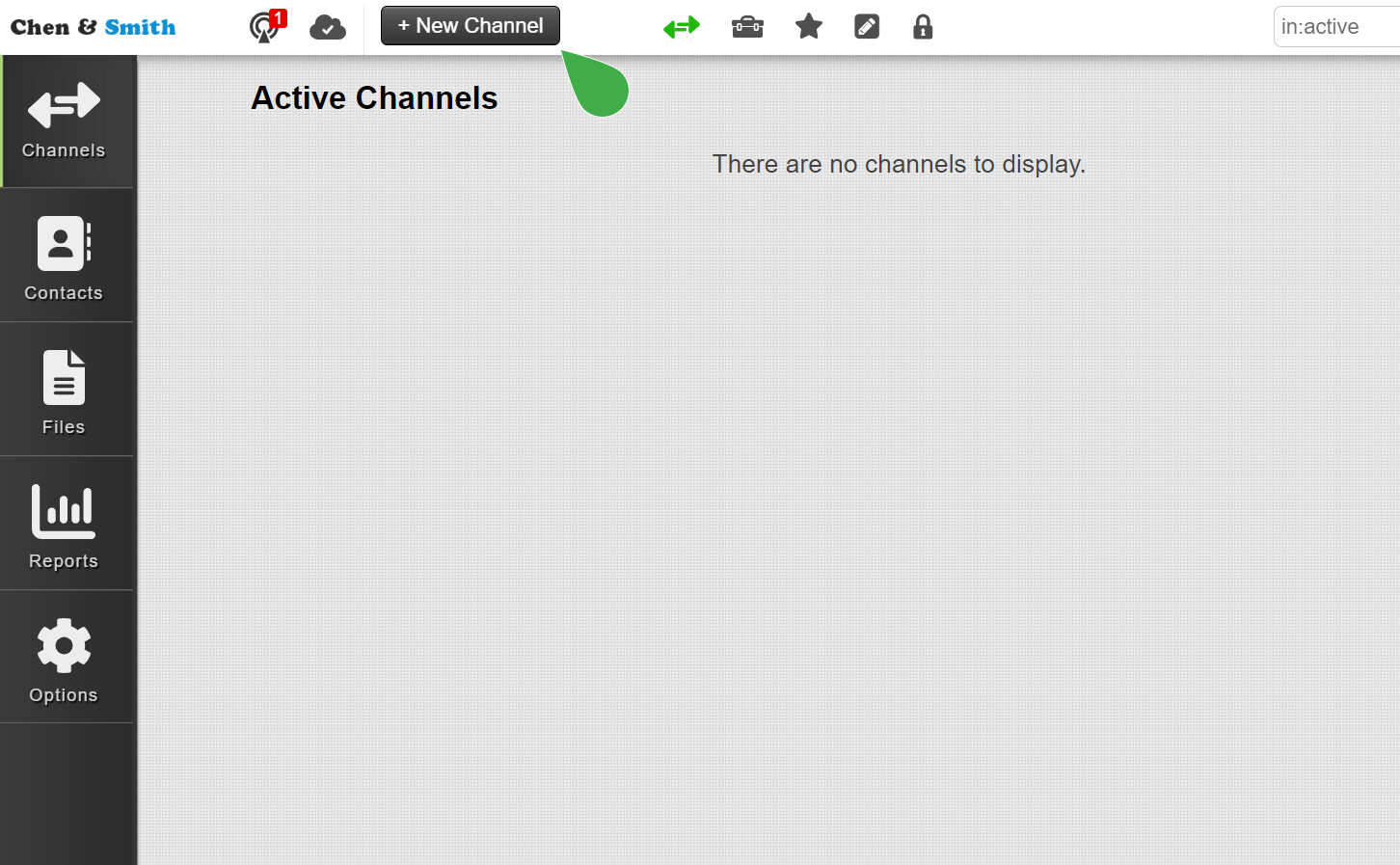
- Sign Up and Create a Channel: Once your account is active, log in and create a new channel by clicking the + New Channel button. This channel becomes your private workspace for sending files to the designated recipient.
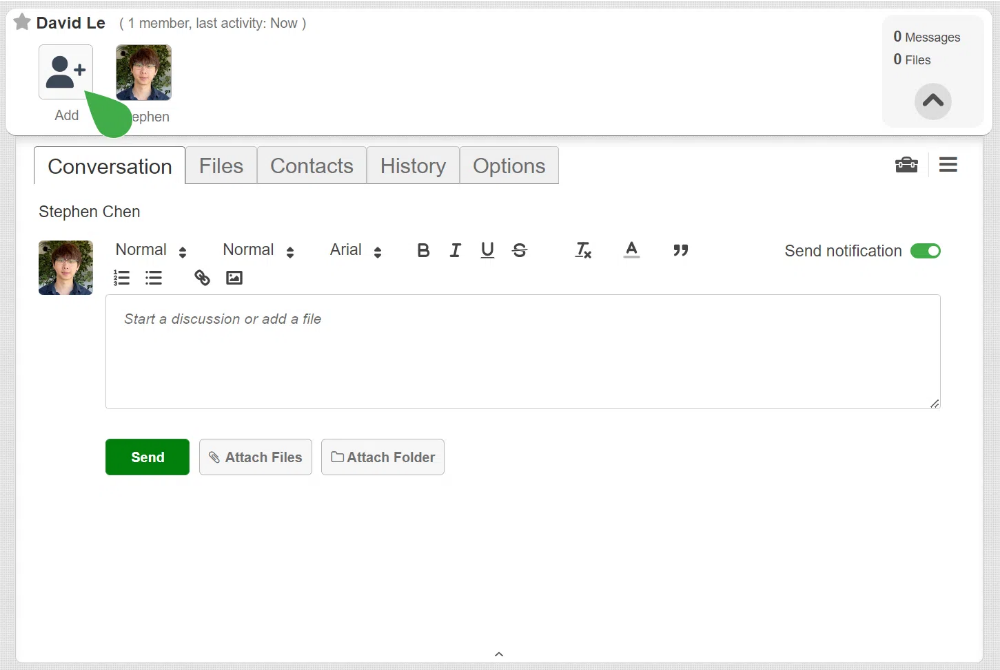
- Add Recipients: To add someone to the channel, click the Add icon and enter the person’s name and email address. You can add multiple recipients, making it easy to collaborate or share files with teams.
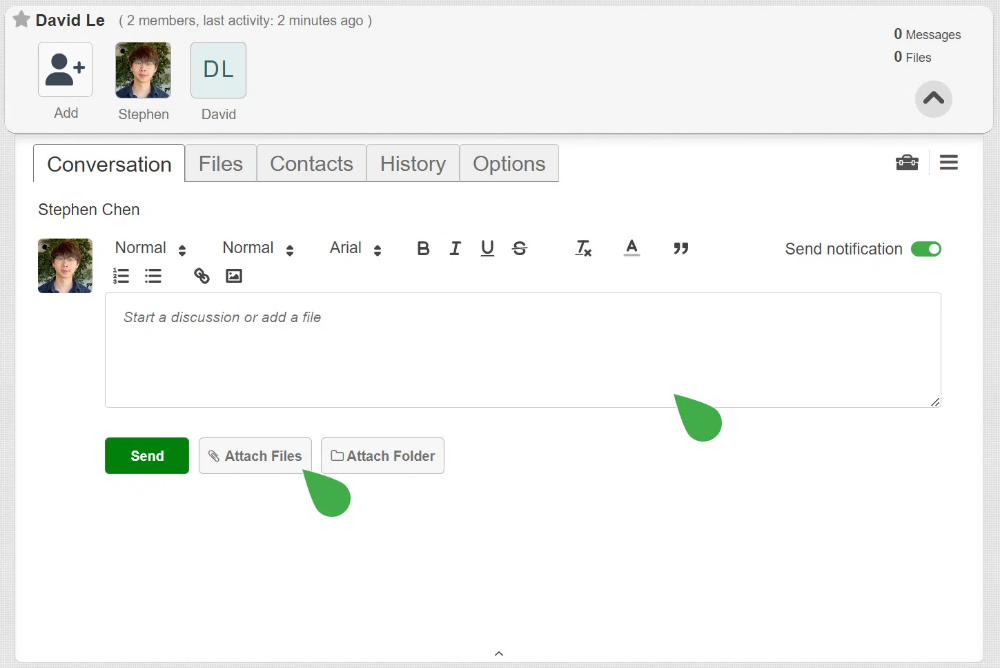
- Attach Files and Messages: After creating the channel and adding recipients, attach your files by clicking Attach Files and selecting the documents you wish to share. You can also include a message in the message box, adding context or instructions for the recipient.
- Send Files: When everything is ready, hit Send. The recipient will receive an email notification with access to the shared files and the option to reply securely.
2. ProtonMail
ProtonMail is a secure email service offering end-to-end encryption, ensuring that only you and your intended recipient can read your messages.
Based in Switzerland, it benefits from strong privacy laws and provides features like self-destructing emails and anonymous sign-up options. ProtonMail is accessible via web and mobile apps.
3. FlowCrypt
FlowCrypt is a browser extension that adds OpenPGP encryption to Gmail. It allows users to send and receive encrypted emails and attachments directly from their inbox. FlowCrypt integrates with Gmail by adding a “Secure Compose” button for easy encrypted communication.
4. Virtru
Virtru offers end-to-end encryption for Gmail and Outlook, allowing users to protect emails and attachments directly within their existing email platforms.
It provides features like access controls, message expiration, and the ability to revoke emails after sending.
Tips for Sending Secure Emails in Gmail
Here are some advanced strategies to send secure emails:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security, 2FA requires a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone, making unauthorized access more difficult.
- Avoid Including Sensitive Details in the Subject Line: Subject lines aren’t encrypted on Gmail, so avoid placing sensitive information there.
- Regularly Review Account Activity: Monitor your account for any unusual activity by checking the “Last account activity” details at the bottom of your inbox. This helps identify unauthorized access promptly.
- Update Recovery Information: Ensure your recovery email and phone number are current to regain access quickly if your account is compromised.
- Be Cautious with Third-Party Access: Review and manage third-party apps connected to your email account, revoking access for any unnecessary or unfamiliar items.
- Send an Email Preview with a Secure Link: Instead of sending the entire message in Gmail, send a preview and include a link to a secure document hosted on an encrypted platform like TitanFile with restricted access.
- Use a Watermark or Notice in the Email: While it won’t stop all breaches, adding a “Confidential” watermark or a note reminding recipients not to share the email can be a gentle deterrent against forwarding or copying.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I send an encrypted email to non-Gmail users?
Yes, you can send encrypted emails to non-Gmail users using Gmail’s Confidential Mode. Recipients will receive a link to view the email’s content and may need to enter a passcode via SMS. However, SMS passcode delivery is limited to certain countries.
What happens if a recipient can’t open an encrypted email?
If a recipient can’t open an encrypted email, it could be due to an expired message, incorrect passcode, or unsupported region for SMS passcodes. In such cases, verify the recipient’s contact information and resend the email if necessary.
Is Gmail’s Confidential Mode truly secure?
Gmail’s Confidential Mode adds security features like expiration dates and access revocation. However, it doesn’t provide end-to-end encryption; recipients can still capture content via screenshots or photos. For highly sensitive information, consider using additional encryption tools.
Do I need to pay for third-party encryption tools?
Some third-party encryption tools offer free versions with basic features, while others require a subscription for advanced functionalities. Evaluate your security needs to determine if the free options suffice or if investing in a paid service is necessary.
Final Thoughts
Many users have transitioned from major email providers to TitanFile due to its user-friendly interface and robust security features. Unlike Gmail’s 25 MB email attachment limit, TitanFile allows you to send large files exceeding 100 GB without restrictions on size or quantity.
TitanFile serves a diverse clientele, including national enterprises in the financial, insurance, and legal sectors, as well as government agencies, regulatory bodies, and small businesses. To experience its advantages firsthand, start a free trial today!