If you’ve ever hit an upload wall trying to send files over 2GB, you’re not alone. Whether it’s a large video, legal brief, or healthcare data package; figuring out how to send files more than 2GB securely and quickly is a modern business challenge.
A study analyzing 49 million files from 348 user collections found that the average file size has increased more than tenfold since the mid-2000s. Yet, most email services still cap attachments at around 25MB. That’s a problem.
So, how do you send a file that’s 2GB, 5GB, or even 50GB? In this guide, we’ll learn the best ways to transfer large files.
Why Sending Large Files Can Be Difficult
Sending big files should be as simple as dragging and dropping. But unfortunately, it’s not. There are a few reasons why it can be a headache:
Email Size Restrictions
A 1080p video file can easily be 4GB to 8GB, way beyond what email platforms allow.
Here’s an overview of the maximum attachment sizes for various providers:
|
Email Service Provider |
Maximum Attachment Size |
|
Gmail |
25 MB |
|
Outlook.com |
20 MB |
|
Yahoo! Mail |
25 MB |
|
ProtonMail |
25 MB |
|
Zoho Mail |
20 MB (Free Plan) |
The email wasn’t built for file transfers. Providers limit file sizes to prevent overwhelming their servers and to reduce spam. Rather than hoping email providers increase limits, it makes more sense to use tools built for the job.
Slow Upload and Download Speeds
Most internet providers prioritize download speeds over upload speeds. That’s because the average consumer spends more time streaming, browsing, and downloading than uploading.
For example, a typical home internet plan might give you 200 Mbps download speed but only 10 Mbps upload speed. That’s fine for everyday use, but if you’re trying to send a 10GB file, that low upload speed will slow your team down big time.
In legal, healthcare, and finance industries, file upload delays can disrupt operations, impact clients, and even create compliance risks.
Security Risks
In 2023, the average cost of a data breach hit $4.45 million, a 15% increase in just three years. That’s a price no business wants to pay.
Transferring large files usually means more risk exposure. Here’s why:
-
A longer transfer means more time for interception.
-
More storage locations (email, cloud servers, local drives) increase attack surfaces.
-
Weak encryption makes files easy to steal if intercepted.
Storage and Bandwidth Limits
Even if you manage to transfer a large file, where does it go? Storage quickly becomes a problem, especially when dealing with massive data.
And what if you delete files to save space? You risk losing important data or needing to re-download massive files later.
Compatibility Issues
Even if you manage to send a large file, will the recipient be able to open it? This is a huge problem in the finance, legal, government, and healthcare industries, where specialized file types are common.
The Best 4 Ways to Send Large Files
Luckily, there are some good ways to send files larger than 2 GB.
Secure File Transfer Platforms
Secure file sharing apps that let users safely send, receive, and store files using encryption and access controls. They protect files from unauthorized viewing or sharing.
They offer some valuable features, such as:
-
Large file size limits.
-
Fast upload and download speeds.
-
Compliance with industry regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA.
TitanFile is the most secure file-sharing solution on the market. It’s as easy to use as email and even includes a Secure Send plugin to encrypt 100% of your email messages and send gigabytes of data without any trouble.
As a secure file transfer service, Titanfile provides:
-
No limits on file size or quantity
-
No storage caps
-
Upload speeds up to 500 Mbps
-
DocuSign integration
-
Document watermarking
-
Secure download links
-
Easy folder and file management
See what Titanfile’s customers have to say about the platform.
Pros
-
Automated security measures
-
Multiple device support
-
Seamless integrations
-
Data retention policies and limits
-
Communication tools available
-
Easily shareable links with password protection
Cons
-
Often require a paid subscription (free trials are available for some platforms)
-
Only suitable for professional use (not suitable for casual users)
Cloud Storage Services
Everyone’s familiar with cloud storage—Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive. These platforms simplify file sharing but still have file size limits, bandwidth caps, and security concerns. For example, Google Drive limits the number of files downloaded per day before it locks for 24 hours.
Free user accounts get small storage quotas, and paid plans have tiered pricing.
Pros
-
Most platforms are already integrated into business workflows
-
Automatically syncs files across devices
-
Paid plans offer scalable storage options
Cons
-
File size limits still apply
-
Security depends on the provider
-
Free accounts come with storage restrictions
-
Some services scan files for policy violations
Read more: The Pros and Cons of Cloud-Based File Sharing
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is one of the oldest methods for transferring large files online. It has existed since the 1970s, long before cloud storage and secure transfer platforms existed.
FTP establishes a connection between a client (your computer) and a server (where files are stored). Once connected, users can transfer files back and forth without worrying about email size limits or cloud storage restrictions.

However, FTP has security weaknesses. It also requires setup and technical knowledge.
Pros
-
No file size limits
-
Full control over data
Cons
-
Traditional FTP lacks encryption
-
It requires technical knowledge to set it up and use it effectively.
-
It is not as convenient as cloud storage for everyday users.
-
If server bandwidth is limited, large transfers can slow down.
USB Drives and External Storage
Even with cloud storage and high-speed internet, companies still rely on USB and external hard drives to transfer large files.
USB drives are also widely used in industries with air-gapped systems, where networks are deliberately isolated for security reasons.
But USB drives come with serious risks. In 2022, a Japanese contractor lost a USB drive containing the personal data of nearly half a million individuals.
Worse, USB drives are notorious for spreading malware—one infected drive plugged into a single computer can compromise an entire network. That’s why many cybersecurity teams may restrict or ban USB usage in corporate environments.
Pros
-
No internet required
-
High-speed external SSDs available
Cons
-
Easy to lose or steal
-
USB drives can spread malware between systems
-
No remote access
-
Can degrade over time
|
Feature |
Secure File Transfer Platforms (TitanFile) |
Cloud Storage Services |
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) |
USB Drives & External Storage |
|
Maximum File Size |
Unlimited |
Limited (varies by plan) |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Security |
End-to-end encryption, compliance (HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA), secure links, access controls |
Varies by provider, limited encryption |
Traditional FTP lacks encryption |
Vulnerable to loss, theft, malware |
|
Upload & Download Speeds |
Very Fast (up to 500 Mbps) |
Moderate to fast (depends on plan and provider) |
Varies by server bandwidth |
Very fast (especially SSDs) |
|
Convenience |
High (easy interface, integration, plugins) |
High (widely integrated, syncs automatically) |
Low (requires technical setup) |
Moderate (physical handling required) |
|
Compliance & Audit Logs |
Yes (Audit logs, document watermarking) |
Limited (depends on provider) |
Yes |
No |
|
Remote Access |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Integration & Compatibility |
High (integrates with DocuSign, Outlook, etc.) |
High (integrated in business workflows) |
Low (manual integration) |
None |
|
Cost & Subscription |
$20 per individual per month with no contracts. |
Free and tiered paid plans |
From 0 (for do-it-yourself ) to thousands of dollars (For full FTP server configuration). |
One-time purchase |
How to Choose the Right File Transfer Method
The best way to send large files depends on your specific needs. If security is your top priority, a secure file transfer platform like TitanFile is the safest choice.
Titanfile encrypts files, offers unlimited storage, and provides fast upload speeds—perfect for industries like healthcare, finance, and law, where sensitive data needs strong protection. It even lets you send larger files via email attachments through an Outlook plugin.
Here’s a screenshot from Titanfile’s platform:
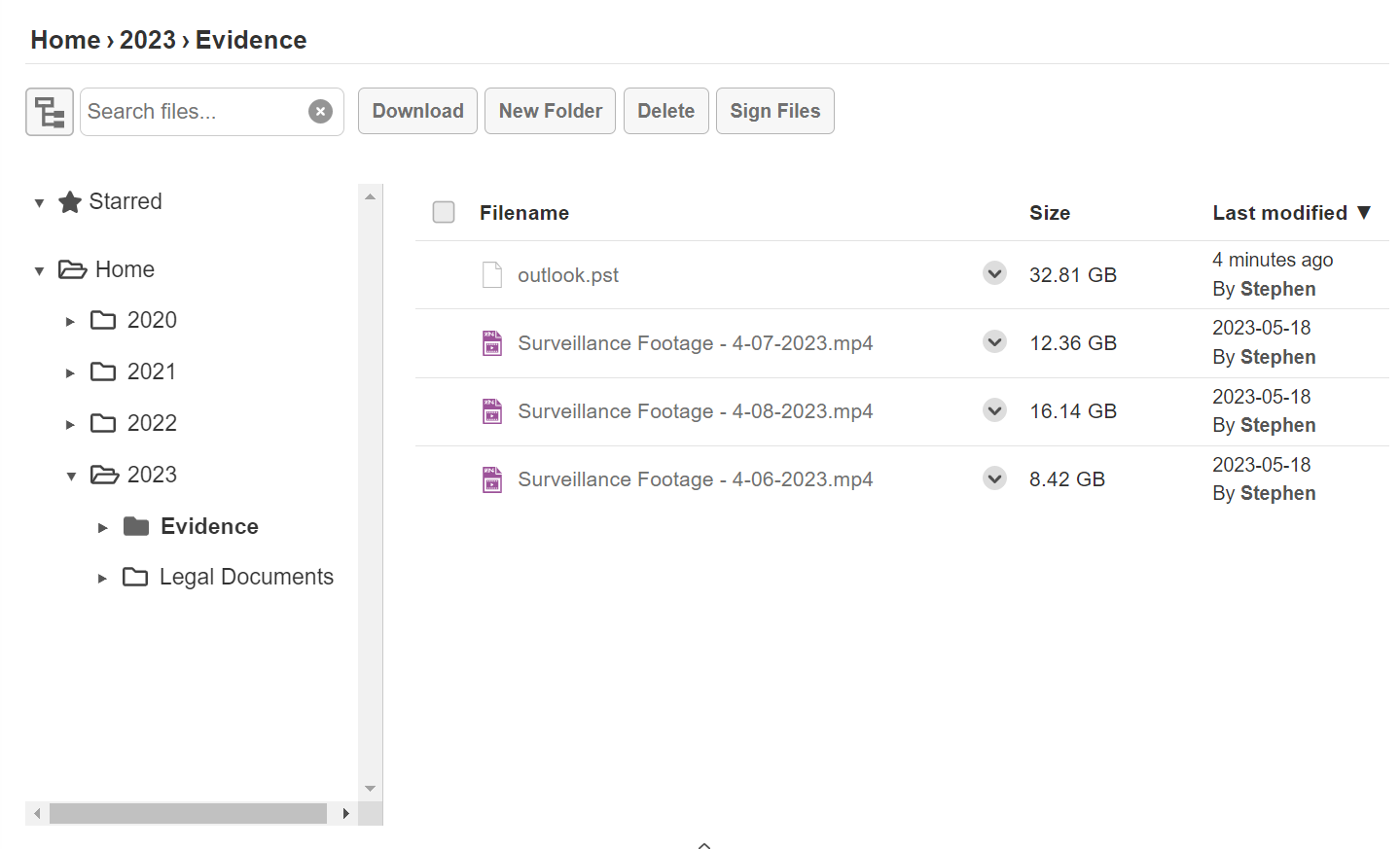
For everyday business file sharing, cloud storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox work well. They’re great for personal use but have file size limits, bandwidth caps, and security concerns.
If speed and offline access are critical, USB drives and external storage remain useful, especially for massive datasets.
At the end of the day, secure file-sharing platforms like TitanFile are the most recommended for businesses that need a balance of security, speed, and ease of use.
Conclusion
Most people default to email or free cloud services because they’ve always used them. But these methods weren’t ideally built for sending large files.
But large files often contain important data, and the wrong transfer method can expose it to security risks, failed uploads, or lost files.
If you’re tired of hitting file size limits, slow uploads, or security risks, try TitanFile. No size restrictions, fast transfers, and full encryption. Start your free 14-day trial today!


