About 30% of internet users have had their data stolen because of weak passwords, nearly one in three people. This is not only because people use “123456” as their password, but also because they alone aren’t cutting it anymore.
With the rising amount of online accounts and web-based footprint comes the rise of more cyber criminals. Even if it’s just your email, your Facebook profile, or your deserted Twitter account, they will stop at nothing to claim it as their own. Whether you’re just a commoner or a big personality, hacks and data breaches will reach you one way or another.
Fortunately for you, business and individual accounts are entitled to add an extra layer of protection. This extra level is called ‘two-factor authentication’ or what’s referred to as 2FA in the online realm. There are plenty more practices that can protect your account, but 2FA stands tall on the email security list.
Let’s discuss how two-factor authentication works, when to use it, and its pros and cons.
What is Two-Factor Authentication?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires users to provide two different forms of identification before gaining access to an account or system.
In 2010, Google introduced its 2FA system, initially for business accounts, and expanded it to all users in 2011. This move set a precedent, leading other major companies like Microsoft, Twitter, and Apple to offer similar security features.
For example, you log into your bank app with your password (the first factor). Then, you get a code sent to your phone and enter that, too (the second factor). Only after both steps are complete can you access your account.
TitanFile takes that same principle and applies it to professional file sharing. With TitanFile, 2FA can be enabled not just for your account but also for your recipients. That means you’re protected if your password is ever compromised. With audit trails, you can also confirm that the person accessing your files is who they say they are.
How Does 2FA Work?
After you enter your password, the system asks for one more thing. That “thing” usually falls into one of three buckets:
- Knowledge-based: a PIN or the answer to a security question.
- Possession-based: Your phone, a text code, an app notification, or a security key.
- Inherence-based: Your fingerprint, face scan, or voice.
So, even if someone has your password, they still need that second factor. And unless they also have your phone or your thumb, they’re out of luck. 2FA dramatically lowers your chances of getting hacked.
MFA vs 2FA
2FA stands for two-factor authentication. Users have to prove their identity with their password and one extra step. MFA means multi-factor authentication. That could mean two, but it could also mean three or more. All 2FA is MFA, but not all MFA is 2FA.
The Importance of Two-factor Authentication
In the past few years, there have been a couple of platforms that have reported data breaches and lost their users’ personal data. Given that technology has progressed further than before, cybercrime has also evolved to become even more polished. If a company decides to give in to traditional practices, it would be more vulnerable to attacks and external threats. As has been said, cybercriminals know no boundaries. Whether you’re a global company with multi-million dollar stakes or a start-up venture, leaving a gap in your security will undoubtedly cause both financial and reputational loss–the beginning of the end, per se.
With no questions asked, what comes after a data breach is an unimaginable defeat. You see, these breaches are but catalysts for identity theft and so much more crimes. For one, stolen credentials result in fake credit cards and worse, shopping sprees. These shopping sprees aren’t your normal visits to Topman or American Eagle there are hundreds of thousands lost in your account. In fact, these data breaches are basically 65% identity theft and because of that, more than $56 billion were lost in 2020
Numbers speak, don’t they? But this is the type of security online platforms have nowadays. In any case, these platforms should offer the tightest, if not tighter, security to their consumers. However, platforms are not the only ones that should move. Consumers, on the other hand, should also be aware of protecting their information, and just one single password isn’t going to cut it. You need one more layer, perhaps something stronger, and most consider that to be two-factor authentication or 2FA security.
Take Siskinds, a full-service law firm that’s been around since 1932, with over 250 legal professionals across four offices. Like many firms, they struggled with a common problem: staff needing IT support just to send files securely. Some even turned to unsanctioned tools just to get work done faster, putting client data at risk.
That’s where TitanFile helped shift the entire workflow. After testing different options, they chose TitanFile for its self-serve simplicity, state-of-the-art security, and built-in two-factor authentication.
Here’s what changed:
- 90% user adoption in the first year
- Staff could share files instantly even 50GB litigation packages without IT help
- Client confidence grew knowing 2FA was securing their sensitive documents
- The IT team finally had room to focus on more strategic work
“The TitanFile platform was a one-stop shop for all of the firm’s file sharing needs.” — Steven Mueller, CIO at Siskinds.
The Benefits of Two-factor Authentication
Passwords are the necessary primary line of defense for keeping your personal accounts safe, but strong passcodes are difficult to keep track of. Too many people fall into the trap of using ones that are easily remembered. It might come as no surprise that the most used password in 2020 ranked by NordPass is ‘123456’. Accounts using that password have already been breached over 23 million times.
2FA is one of the most dependable security measures that can cater to everyone. If you have 2FA by your side, not even your password is enough to breach your account. Even if someone guessed your impossible password, it’s unlikely that they’ll have access to the secret code that was sent to your phone or know the name of your neighbor’s dog. If more platforms enforced security measures like this, they’d be worrying more about improving their systems instead of data breaches.
There are a few other benefits to TFA as well. Professionals will be happy to know that it fills compliance requirements for PCI, HIPAA, and PIPEDA if you ever need to transfer any protected health information. Additionally, two-factor authentication makes remote working a little safer for those days you can’t make it in to work.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
Eventually, you’ll realize that your only form of protection is your password. By then, hopefully, you would’ve understood that there’s a great chance of being hacked. This realization may lead you to either strengthen your password to a point of no return or just getting or enabling yourself the two-factor authentication system. If you’ve chosen the latter, then accept that you will be offered pristine security for your account and eliminate the chances of being hacked.
Though this may be true, that doesn’t mean that all two-factor authentication is the same in strength value. Currently, there are multiple platforms that utilize multiple types of 2FA, and their strength varies from one another, but rest assured that it’s definitely better than your lonely passwords. Here are all the types of 2FA!
Hardware Tokens
 Way older than you’d expect it to be, hardware tokens look more like advanced key fobs than 2FA tools. It generates a new numeric code every 30 seconds, and when someone tries to access an account, all they have to do is look at the number combination and enter it on the site. There’s another version of the hardware token wherein it automatically transfers the 2FA code as long as it’s plugged into the USB port.
Way older than you’d expect it to be, hardware tokens look more like advanced key fobs than 2FA tools. It generates a new numeric code every 30 seconds, and when someone tries to access an account, all they have to do is look at the number combination and enter it on the site. There’s another version of the hardware token wherein it automatically transfers the 2FA code as long as it’s plugged into the USB port.
Though this did offer some form of security, it just wasn’t feasible for businesses to distribute it left, right, and center. These units are costly, and distributing them is even costlier. The danger of losing it or getting it stolen are real possibility as well.
SMS or Message-based and Call-based 2FA
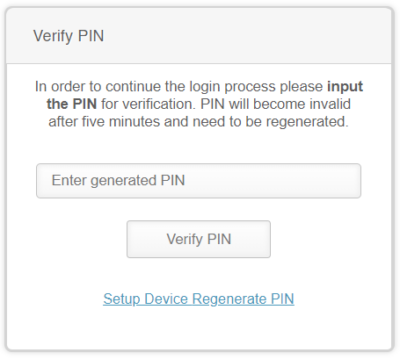 Message-based 2FA directly sends you the code to your phone through SMS. Essentially, the platform sends the user a unique one-time passcode (OTP). Similar to the hardware token, this OTP must be typed into the platform to gain access to your account. As for call-based or voice-based 2FA, it calls the user and verbally says the 2FA code. Don’t worry, it’s just a robot speaking. Smartphone supply-and-demand proves to be an obstacle for this 2FA, but it still functions albeit uncommonly.
Message-based 2FA directly sends you the code to your phone through SMS. Essentially, the platform sends the user a unique one-time passcode (OTP). Similar to the hardware token, this OTP must be typed into the platform to gain access to your account. As for call-based or voice-based 2FA, it calls the user and verbally says the 2FA code. Don’t worry, it’s just a robot speaking. Smartphone supply-and-demand proves to be an obstacle for this 2FA, but it still functions albeit uncommonly.
Many have described SMS-based 2FA to not be enough protection, though. Hackers are able to spoof a phone number and intercept a 2FA code. Still better than not having 2FA at all.
Software Token / Authenticator Apps
 Two-step authentication, 2-step Verification SMS code password concept. Smartphone with special 2FA software and tablet pc with multi-factor authentication safety and secure login form.
Two-step authentication, 2-step Verification SMS code password concept. Smartphone with special 2FA software and tablet pc with multi-factor authentication safety and secure login form.
This form of two-factor authentication is, quite possibly, what tops the podium. It’s like a combination of the last two 2FA types wherein a software-generated and time-based OTP is given to the user.
In a way, it’s like the hardware token where the code only lasts for less than a minute. Combined with the convenience of SMS-based 2FA where it just goes directly to your phone, it’s 2FA innovation at its finest.
The way it functions is particularly different. The user must first download and install a free 2FA app like Authy, Google Authenticator, or Vonage on their phone and/or computer. This app works for any platform that supports two-factor authentications. After signing in, the app shows a code that serves as your OTP. What makes it better than SMS-based 2FA is since the code is both generated and displayed on the same device and app, it’s less prone to being hacked.
Since this app-based 2FA solution is available just about anywhere from your phones, laptops, desktops, and other gadgets, and even offline, this makes for one of the best two-factor authentications to exist in the current time.
Push Notifications
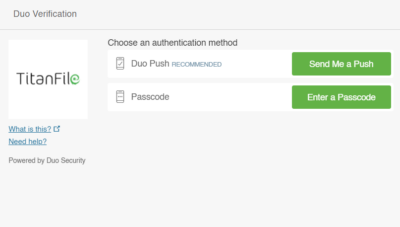 For the past three 2FA types, all of them choose to utilize a code as a means of security. Push notifications take it a step further, though. Before anything else, push notifications are messages that pop up on your mobile device. Similar to text messages, app publishers are able to send them at any time, and the users don’t have to access the app to receive or see them.
For the past three 2FA types, all of them choose to utilize a code as a means of security. Push notifications take it a step further, though. Before anything else, push notifications are messages that pop up on your mobile device. Similar to text messages, app publishers are able to send them at any time, and the users don’t have to access the app to receive or see them.
As a 2FA method, push notifications function very differently than the other 2FA methods we’ve described. Users can use apps like Duo to allow or deny access with just a single touch no codes, no passwords, and takes no more than 5 seconds.
Inherently, this is a relationship between the app and the user. This eliminates threats of being hacked or having cybercriminals in the middle of your business. Push notifications as 2FA security is very much effective user-friendly, too.
Biometrics
 This form of two-factor authentication isn’t as well-versed as the ones that came before it. However, it’s only a matter of time until the online audience is able to use their fingerprints, retinas, and facial recognition to access their accounts. Either way, it’s already possible as a means to open your phone. This sounds neat and all, but biometric hackers are already wary of how this might be the most powerful 2FA there is.
This form of two-factor authentication isn’t as well-versed as the ones that came before it. However, it’s only a matter of time until the online audience is able to use their fingerprints, retinas, and facial recognition to access their accounts. Either way, it’s already possible as a means to open your phone. This sounds neat and all, but biometric hackers are already wary of how this might be the most powerful 2FA there is.
Passwordless 2FA
Passwordless 2FA skips the traditional login step and uses two other factors instead. For example, you might click a login link sent to your email address (something you have), then use your fingerprint (something you are) to confirm it’s you.
In many ways, passwordless 2FA is the future. It solves one of the most significant problems with traditional security: people reusing weak passwords across many accounts. If you remove the password, you remove that whole risk. The downside is that it often relies on your phone. You’re locked out if you lose your phone or it gets stolen.
Knowledge Factors
In two-factor authentication, knowledge factors are things only you should know. That could be:
- Your password
- A PIN
- The answer to a security question
These factors aren’t as widely recommended today, mainly because many users struggle to remember or keep them secure.
Possession Factors
Possession factors are all about something you have. It’s a physical device that proves it’s really you trying to log in. Think of things like your smartphone, laptop, or a security key (like a YubiKey).
Behavioural Factors
Behavioural factors are based on how you do something. This is newer in the two-factor authentication space, but it’s starting to grow.
Examples include:
- The way you type
- How you swipe on your phone
- Your usual location or time of login
- How you move your mouse
These systems learn your patterns over time. So, if someone suddenly tries to log in from a different country or is typing way slower than you usually do, the system might flag it or block it entirely.
Behavioural 2FA works quietly in the background and doesn’t get in your way.
Potential Downsides to Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is an excellent way to protect your organization and clients’ online privacy. But that doesn’t mean it’s perfect.
Some hackers use phishing to trick you into giving up your password and second factor. Others might hijack your SIM card to intercept text codes.
In June 2018, Reddit suffered a data breach. Attackers accessed user emails, internal files, source code, and data from 2007 and earlier. The breach was facilitated through intercepted SMS-based two-factor authentication (2FA) verification codes.
Here are a few more disadvantages of two-factor authentication to keep in mind:
- It can be annoying: Extra steps mean more friction. If you’re in a rush or have a poor signal, that code might not come through fast.
- You can get locked out: Recovering access isn’t always easy if you lose your phone.
- False lockouts. Behavioural 2FA or location-based checks might lock you out just for logging in from a different city or using a new device.
How 2FA Works With Other Authentication Tools
Two-factor authentication doesn’t work alone. It’s usually part of a bigger security setup. Let’s go over how 2FA fits into the bigger picture:
Single Sign-on (SSO)
Single sign-on (SSO) lets you log in once and access multiple apps or services without entering your password every time.
If your one SSO login gets compromised, everything connected to it could be at risk. That’s why adding 2FA to your SSO login is crucial. It adds a second layer before anyone can access your entire system.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
2FA is a type of multi-factor authentication that uses exactly two factors, like a password plus a text code. MFA can use two or more, so 2FA is the most common version of MFA.
Risk-Based Authentication
Risk-based authentication takes things a step further. It looks at how risky a login attempt is, and then decides if it needs more verification.
Let’s say you usually log in from Toronto, but suddenly, there’s a login from another country at 2 a.m. The system sees that and asks for extra proof, like a 2FA code or biometric scan.
Secure Remote Access
When people work from home or log in from outside the office, things get tricky. Secure remote access tools help protect your network from threats through personal devices or public Wi-Fi. But they’re not complete without 2FA.
Adding two-factor authentication ensures that anyone logging in remotely is who they say they are.
Security Training and Awareness
None of this matters if your team doesn’t understand how to use it. You can have the best 2FA system in the world, but you’re back to square one if someone falls for a phishing attack email and gives up their code.
Teach your users about 2FA, how to spot fake login pages, and why they shouldn’t approve random push notifications.
Examples of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Here are a few solid examples of platforms using two-factor authentication:
TitanFile
TitanFile is a secure file-sharing and client collaboration tool used heavily by legal, accounting, and healthcare professionals.
TitanFile gives users several ways to verify their identity for two-factor authentication: SMS codes, voice calls, emails, authenticator apps, and even Duo push notifications. That flexibility means organizations can pick the method that fits their workflow and keep things locked down.
It supports popular authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Duo Mobile Security.
Alberta Netcare (Canada)
Alberta Netcare works in the healthcare sector based in Alberta, Canada, to store patient records. The system uses two-factor authentication to protect that data: users log in with their usual credentials plus a physical RSA SecurID key fob that generates a time-based code.
Everlaw
Everlaw is a platform for e-discovery, which involves organizing and reviewing legal documents during lawsuits.
Everlaw requires two authentication factors to keep client data secure. After entering a password, users must also enter a secondary code sent to them by email or phone.
Protect What Matters With Titanfile’s 2FA
If your organization handles sensitive documents or confidential communication, you need more than basic security. You need a system built with protection at its core, i.e., secure, flexible, and easy for everyone to use.
TitanFile checks all those boxes. It gives professionals in law, accounting, and healthcare the power to share files and collaborate with clients securely, with two-factor authentication. We store all data in Canadian data centers, ensuring compliance with national privacy laws.
Don’t wait for a breach to take security seriously. Try TitanFile today!


